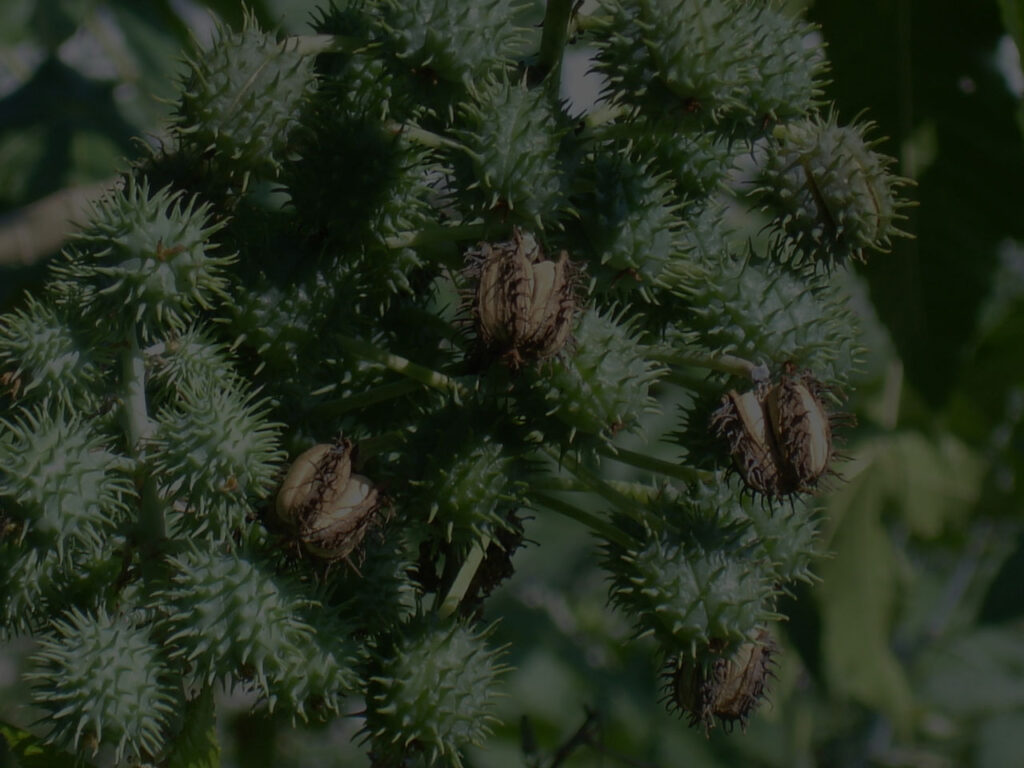
castor bean

The castor bean culture
• Does not compete with food crops
• Is planted in Brazil as a second crop, after food crops
• Is drought tolerant
• Helps in reducing the multiplication of soil nematodes
Castor bean is an oleaginous plant for exclusive industrial use, whose main product, castor oil, opens up a range of possibilities for obtaining different derivatives
Castor
The transformation of vegetable oils is being widely used in green chemistry seeking to obtain existing products, usually obtained from petroleum, by products obtained in a more sustainable way.
From the early 2000s, the demand for castor oil has increased among industries due to its bio-degradability. Among many sustainable and biodegradable products, castor oil is one of the best industrial material due to its efficiency, availability and cultivation.
In addition to its renewability and biodegradability, castor oil brings many benefits.
• Enable industries to follow eco-friendly practices
• Sustainable growth in business
• Utilize green energy or clean energy
• Ensure carbon saving
• Not competing with food
Since castor oil has a high boiling point and viscosity, it has a huge potential as a bio-based chemical resource. It is considered to be an essential raw material during manufacturing in many industries including special plastics, paints, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, dyes, aniline, disinfectants, germicides, low temperature lubricating oils, glues and adherents; serves as the basis for fungicides, insecticides, printing inks, varnishes, nylon and plastic material.
Castor oil is extracted from castor beans by different extraction methods such as mechanical pressing, solvent extraction and also a combination of pressing and chemical extraction.
The main products derived from castor oil are:
• Castor oil no. 1.
• Dehydrated castor oil.
• Dehydrated castor oil GH.
• Dehydrated castor oil distilled fatty acid.
• Castor oil crude fatty acid.
• Acid 12-hdroxide stearic.
• Castor oil methylester.
• Castor oil sulfuricoil.
• Hydrogenated castor oil.
Castor Cake
Castor cake, obtained in the industrial oil extraction process, is another valuable product of direct application in agriculture as organic fertilizer
The main nutrients of castor cake are:
• Nitrogen 4.5%. • Calcium 2.5%. • Phosphorus 1.6%. • Potassium 1.3%.
In addition to meeting the nutritional needs of plants, castor cake decreases soil acidity and has insecticide and nematicide properties.
Although it has a high protein content, castor cake cannot be used as animal feed because it presents highly toxic compounds, whose inactivation is being studied.
seed production in the Uberlândia region
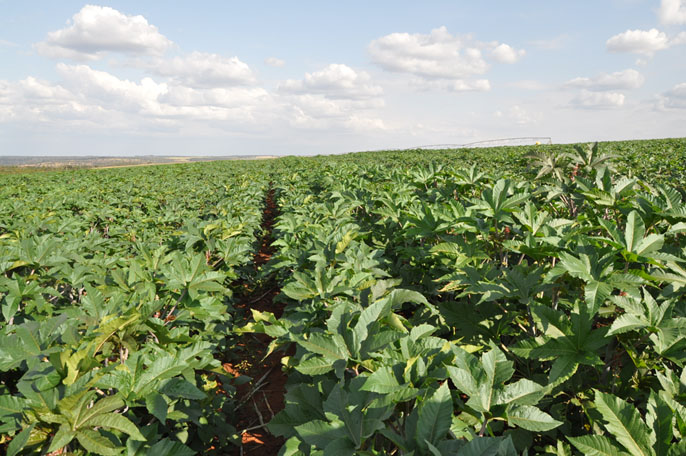

Experience acquired with the production of hybrid castor seeds in irrigated areas since 2014, for sales in Brazil and other Latin American countries
Terasol agricultural model
- High performance hybrid castor seeds
- Large areas
- Professional producers
- Mechanization
- Planting after soybean harvest
- Productivity
- Best agricultural practices
- Attractive financial return
- Nematode control
The West of Bahia presents opportunity both in irrigated and dry areas
In dry areas we recommend planting to receive at least 400mm of rain in the first 60-70 days after germination (ideal planting in the Garganta Region/BA in February for harvesting in June)
In irrigated areas we understand that castor enters as an alternative of second crop, with planting in March /April and harvesting in July/August
In Mato Grosso, castor crop enters as a second crop option after the soybean harvesting (ideal planting in early March for harvesting in July)
mechanized harvest
- Available platforms for harvesting castor bean:
world castor oil market
World market for castor oil in 2019/2020: approximately 930 thousand tons, equivalent to more than US$ 1.2 billion
Demand for large volumes of castor oil is repressed; great opportunity for Brazil
INDIA – world leader in the production and export of castor oil: 92% of world production and 96% of world exports
Main world importers of castor oil: Europe, United States and Asia
Great opportunity for Brazil
Brazil is set to compete with India
Brazil has large extensions of land ready for castor
• World-class agribusiness, with top technology
• Central states plant 2 crops per year (Oct-Jan and Feb-Aug)
• Mato Grosso State alone has 3MM ha idle in second crop
• Bahia State has large areas, many irrigated
• Terasol and others produce high quality hybrid seeds for dwarf plants
• Mechanical harvesting available and improving
• Trend is for exponential growth
Challenges for the coming years
Mechanized harvesting with losses less than 5%
Expansion of agricultural area with castor bean in Bahia and Mato Grosso
Castor oil production in Bahia and Mato Grosso